I have written before about “Mad Jack Howard”, the Earl Of Suffolk who was posthumously awarded the George Cross for his EOD activities in WW2. (and I’ve also written in more detail about his adventures in Europe as the Germans invaded France where he rescued a large amount of Heavy Water)
There was fellow Lord, Lord Rothschild, who was also an EOD specialist, (amongst many other things) and another remarkable character undertaking specialised bomb disposal operations in WW2. Rothschild was awarded the George Medal of defusing a German sabotage device recovered from the hold of a ship, hidden in a crate of Spanish onions. At the time he ran a small department within MI5 responsible for examining the threat from German sabotage devices. They conducted sabotage threat assessments and investigated sabotage devices. I’m waiting for permission from the Rothschild estate to publish an excerpt from his book, a transcript of a telephone call he made, live, to his secretary, describing the render-safe procedure of the “onion crate” as he went through it, together with some photos..
Beyond that I’m digging into the work of his section (and some other interesting UK WW2 organisations with related activities) and will post when I have enough material.
Rothschild, like Suffolk, was a remarkable polymath and a very interesting character. As well as his EOD work in the UK, he interrogated suspected Nazi saboteurs, and travelled to the US to examine captured explosives and interrogate captured German spies. His detailed report from this US trip is a fascinating read – another case of shared Weapons Technical Intelligence between the UK and US.

One of Rothschild’s key findings in this report on the German saboteurs in the US, that he obtained from interrogating the saboteurs commander, Jansch, was that the Germans had decided for future operations that rather than infiltrate complex sabotage devices into the US by submarine, they were moving to a strategy of inserting one or two saboteurs with minimal equipment (just detonators/blasting caps). The saboteurs were instructed to improvise the explosive devices from locally obtained components. So this was by 1943 becoming a real “IED” strategy.
Although the sabotage mission being investigated by Rothschild, at the invitation of the FBI, was well equipped with explosive devices, Rothschild’s interrogation identified that the German saboteurs were trained to improvise devices. For example, they had been trained to create timing mechanisms using such raw material as dried peas, lumps of sugar and razor blades. Rothschild was disturbed by this as it avoided strategies he had put in place in the UK to identify suspicious purchases which could be used for explosive device manufacture such as clocks and certain chemicals. (The latter point presaged modern efforts in the UK to identify purchases of hydrogen peroxide – in those days it was sulphuric acid and potassium chlorate, amongst other material.)
Rothschild’s report makes clear that, like their enemies the Russians, the Germans too had extensive training in sabotage, albeit in this case the saboteurs were a little undercooked. The Abwehr had identified aircraft manufacture as the key strategic capability to be attacked in the US, and consequently their saboteurs had been given special training in understanding the production processes in aluminium and magnesium alloy plants. Interestingly I have also found an SOE manual that provides guidance for systematic sabotage of certain industrial machines and I think there is some interesting and peculiar correlation between, Russian, German and British sabotage guidance for machinery. That too a subject for a future post.
I try to avoid much comment on modern political motivations in these blogs – but I’m struck by the parallels with the German saboteurs in the USA and modern jihadi terrorists:
- Many of the German saboteurs or their families had emigrated to the USA between 1910 and 1930, so in the decades well before the war, so they had intimate knowledge of the USA, and were quite comfortable operating within the USA. Most of them were naturalized US citizens.
- Many joined radical political organisations in the USA, mainly the German-American Bund. So perhaps they were “radicalised” at this point, in some cases.
- Some of them returned to Germany when Germany went to war in 1939 with a motivation to support Germany’s war efforts.
- To some degree the saboteurs were often incompetent.
The German Sabotage School conducted a three week training course, followed by a series of visits to German industrial sites to discuss vulnerabilities to sabotage. Rothschild’s report is fascinating in its detail, even including the pay, pensions and allowances that each saboteur had agreed with the Abwehr.
Rothschild details the home-made explosives and incendiary mixtures that the saboteurs had been trained to put together. They had been specifically instructed in mixes using ingredients that could be purchased from chemist shops in the USA. However it seems that some of the saboteurs forgot some of the mixes, such was their incompetence.
One item of particular note was their instructions to create improvised detonators and the specific mix to achieve such a material. I won’t republish here. Suffice to say it involves peroxide and hexamine, material not unknown to modern terrorists.
Several improvised timing switches are discussed in detail, as is a number of pressure switches. The report also includes diagrams by one of the team. This is an example, (with my redactions) which I’m not going to explain in this forum or clarify the blurry annotation, suffice to say it is an initiation I have never come across before:
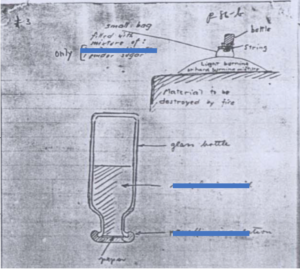
I’m happy to forward the details and all of Rothschild’s report to accredited EOD techs if you ping me. If I don’t know you or your organisation, don’t ask.
I was a little thrown by one technical comment in the report by Rothschild – he lists the explosive components smuggled into the USA by the saboteurs and one is described as follows:

Mercury Fulminate in det cord? Surely not? I welcome any comments. Has anyone come across such a thing? I can’t recall such a thing but there are readers of this blog who may know – please comment.