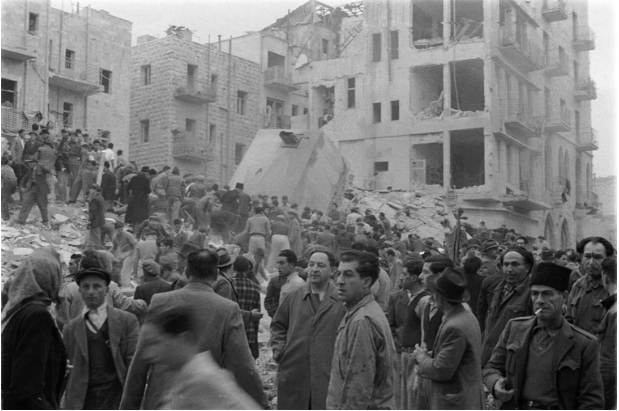
I’ve been researching the improvised explosives used by the Polish resistance in WW2. One can’t but help notice some parallels between the Warsaw uprising and the ongoing tragedies in Syria – the devastation of Warsaw looks pretty similar to that being seen in Aleppo and other Syrian cities. The Nazi destruction of the ghetto is scarily similar to the Assad regime’s destruction of areas of Syrian cities. Compare the effect of the use of the siege mortar “Thor” (Karl-Gerat) against the Warsaw ghetto with the user of barrel bombs in Aleppo.
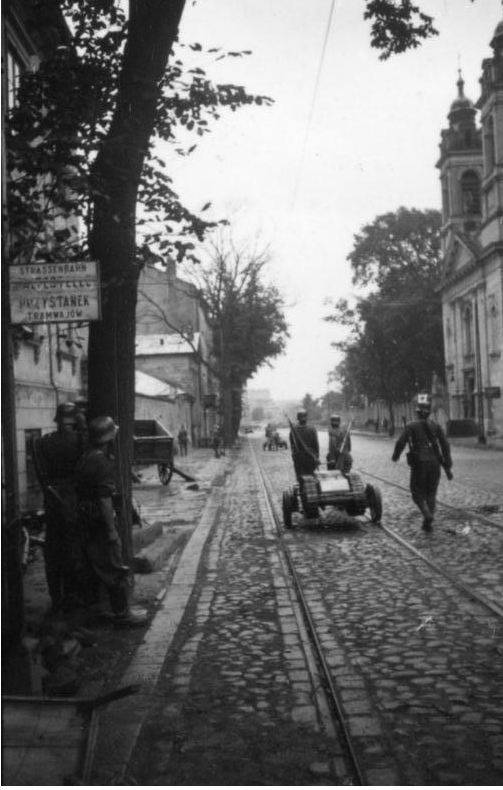
Here’s two interesting images – the black and white one shows a Warsaw resistance fighter examining a “blind” Karl-Gerat munition. The colour image below it shows a Syrian resistance fighter with a “blind” barrel bomb. I’m not suggesting the munitions are identical, but in terms of explosive effect they will have been pretty similar, and it’s spooky how similar the images are, some 70 years apart.

1944

2014
Consider the similarity of effects:
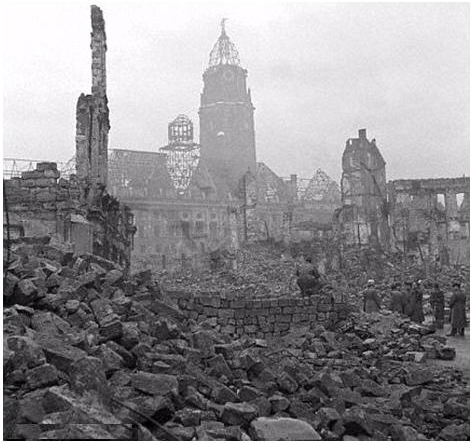

Warsaw
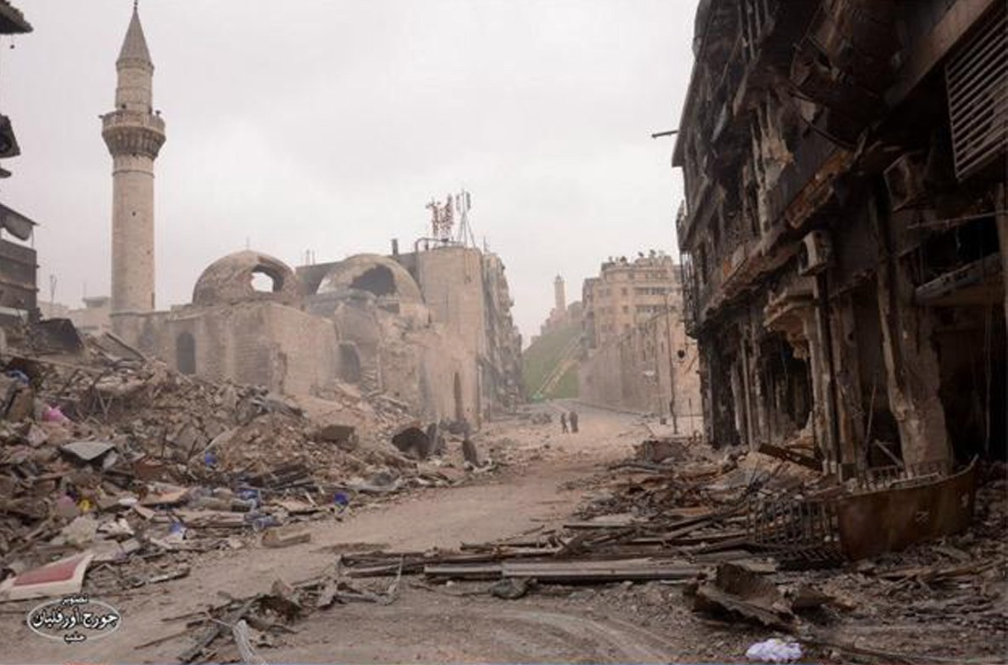

Aleppo
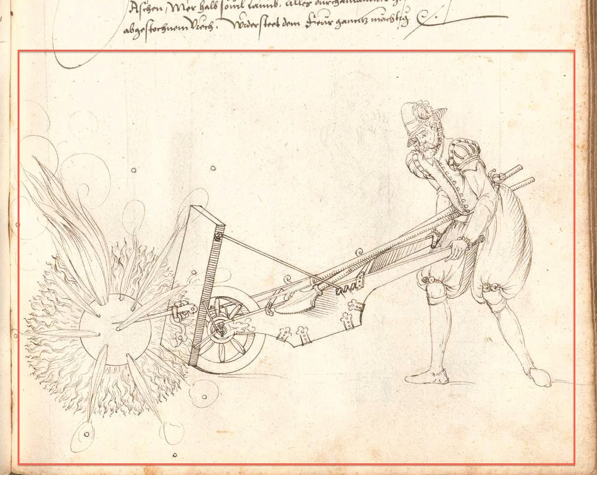
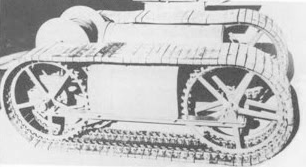
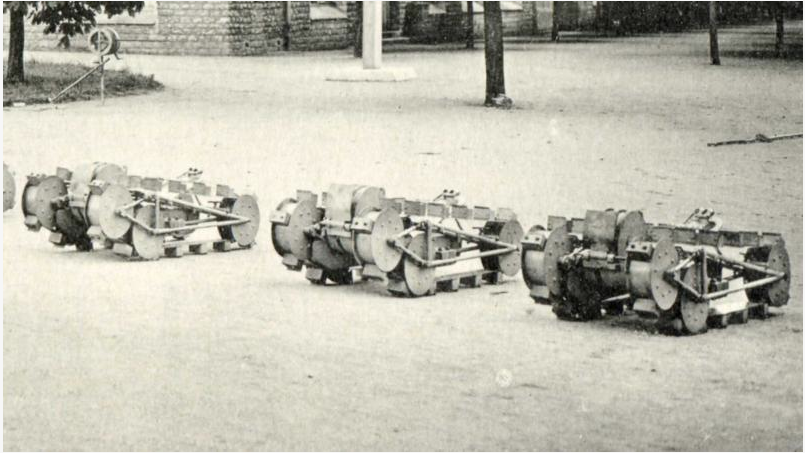
There are other similarities too – the Polish resistance had a very significant production of ingenious improvised weapons – and some of their techniques appear similar too to those seen in Poland. Look at this image of a spring-loaded Molotov cocktail projector – I’ve seen similar from Syria

The boundaries between improvised weapons and production weapons can get a bit vague here – for example its is thought that tens of thousands of Sidolowka and Filipinka grandes were produced by the resistance.
These improvised grenades had a variety of fills, but most commonly “cheddite”, a chlorate/nitrobenzene mix I have discussed in earlier posts (used by many including Irish revolutionaries circa 1920.) Not much difference in design , of course with the Irish grenades seen here…with the same explosive fill. All aspects of the grenade including the fuse and the detonators were produced by the Polish resistance. Largely they obtained the potassium chlorate component of the explosive by theft from the Germans.

An improvised Filipinka grenade. The Cyrillic marking is an attempt by the Polish resistance to obfuscate indigenous manufacture
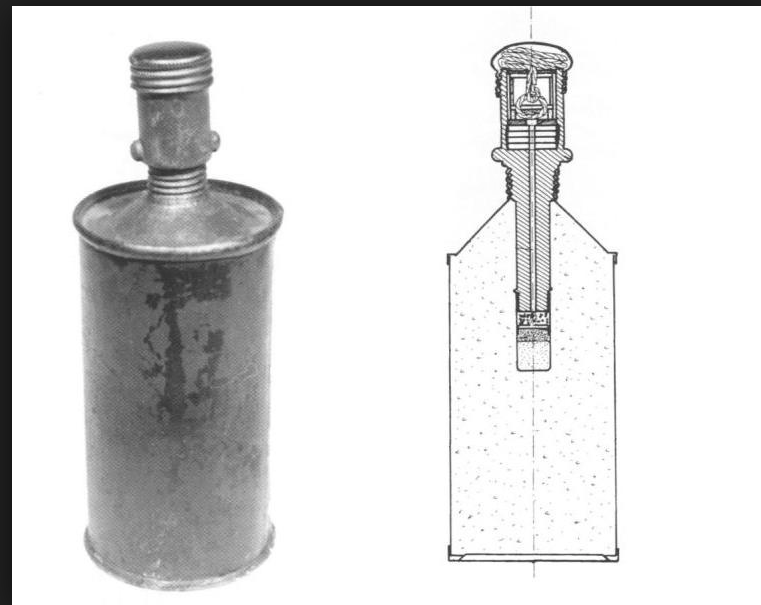

Improvised Sidolowka grenade.
The Polish resistance also made significant use of command wires devices and other IEDs to attack trains and other targets. Here’s a picture of the explosive unit of the Warsaw resistance on route to attacks the Warsaw telephone exchange on 18th/20th August 1944 with a command wire initiated device.

Hundreds of German military trains were attacked with IEDs too. During one six month period the British SOE assessed that the Polish resistance had wrecked 1,268 railway engines and damaged 3,318 carriages. This report describes the operationally sophisticated use of multiple IEDs along a railway line:
An ordinary railway mine, which exploded when the first train passed over it would cause an interruption in traffic for only about four hours. At one time we were anxious to interrupt traffic on the main Warsaw-Malkinia sector of the Eastern front for a minimum period of 10 days. Our experts solved the problem, and the resulting interruption lasted as long as two weeks. It was done by specially devised mines which could be automatically blown up. A chain of these mines was laid across the tracks. The first, which was placed in the middle of the chain, went off as the first train was passing over it. Two more placed on the tracks on either side of the first when the rescue train arrived from one side or the other. The remaining mines on both sides of the wrecked trains exploded successively when the repair trains arrived from both directions. Result: Ten miles of track effectively mined. After their first train has been blown up four repair and relief trains sent in to deal with it had been effectively destroyed.
Other sophisticated IEDs were also created by the Poles. I have found one report that 18 Luftwaffe aircraft were destroyed by the use of an explosive device in an elongated cylinder which was hidden in the rear of German aircraft and initiated on a reduction of atmospheric pressure once the aircraft reached a certain height.









 Roger Davies
Roger Davies